文章信息
Tang, Y., Zhang, J., Liu, R., Li, Y., 2022. Exploring the Impact of Built Environment Attributes on Social Followings Using Social Media Data and Deep Learning. IJGI 11, 325.
论文摘要
街道是城市景观的重要组成部分,反映了公共空间的形象、生活质量和活力。在Cityscapes城市数据集和DeepLab-v3深度学习模型的帮助下,我们对全景图像进行了分割,以获得视觉统计数据,并分析了建筑环境属性对餐厅人气的影响。结果显示,餐厅的评价受到交通标志密度、行人流量、自行车慢行指数和地形变化的影响,其中交通标志密度与评价数量有明显的负相关关系。影响餐厅食品、室内环境和服务评价的最关键因素是人流量,其次是道路步行性和自行车慢行指数,然后是自然要素(天空开阔度、绿化率和地形)、交通相关因素(路网密度和机动车干扰指数)和人工环境(如建筑率),而人们的停留意愿对评价有明显的负面影响。影响人均消费的建筑环境质量包括交通标志密度、人流量和非机动车设计程度,其中交通标志密度的影响最为明显。
Abstract
Streets are an important component of urban landscapes and reflect the image, quality of life, and vitality of public spaces. With the help of the Google Cityscapes urban dataset and the DeepLab-v3 deep learning model, we segmented panoramic images to obtain visual statistics, and analyzed the impact of built environment attributes on a restaurant’s popularity. The results show that restaurant reviews are affected by the density of traffic signs, flow of pedestrians, the bicycle slow-moving index, and variations in the terrain, among which the density of traffic signs has a significant negative correlation with the number of reviews. The most critical factor that affects ratings on restaurants’ food, indoor environment and service is pedestrian flow, followed by road walkability and bicycle slow-moving index, and then natural elements (sky openness, greening rate, and terrain), traffic-related factors (road network density and motor vehicle interference index), and artificial environment (such as the building rate), while people’s willingness to stay has a significant negative effect on ratings. The qualities of the built environment that affect per capita consumption include density of traffic signs, pedestrian flow, and degree of non-motorized design, where the density of traffic signs has the most significant effect.
文章下载链接
https://www.mdpi.com/2220-9964/11/6/325
研究框架
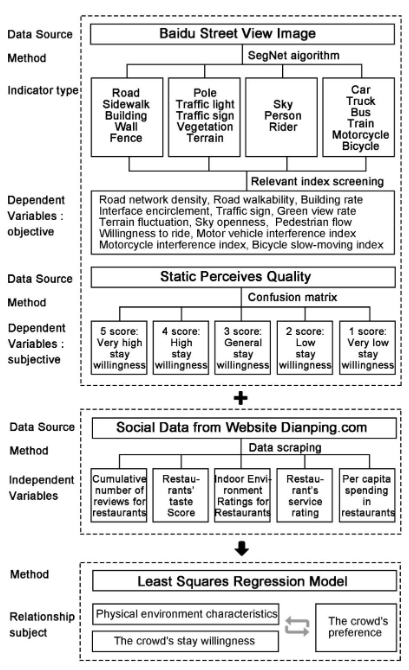
本研究以餐饮点为例,(1) 使用上海内环路内的BSV全景图,用语义分割的方式量化了可见街道的构成。(2) 比较了多个深度学习模型的停留意愿的混淆矩阵结果,并选择预训练Inception-v4模型对8220张街道全景图进行1-5级的停留意愿推理。(3) 利用爬虫程序提取大众点评网的数据,获得人们对餐厅用餐体验的评价;利用ArcGIS 10.6对上海内环线内的21065家餐厅的类型、评价数量、消费者的口味评价、室内环境评价、服务评价、人均消费等进行可视化。(4) 根据数理统计中的3σ原则,剔除了三个标准差之外的数据,得到最终选择的16794个数据项。(5) 在坐标的基础上,对物理空间的环境质量、人们的停留意愿和地方知名度进行了最小二乘回归分析。最后,对餐厅周围的物理环境特征、人们的停留意愿评价和人们的喜好之间的关系进行了量化,为优化土地利用、提高特大城市的宜居性、保证城市高质量发展提供参考。